: Coinsurance is a percentage of the expense of your medical care. For an MRI that costs $1,000, you might pay 20 percent ($ 200). Your insurance company will pay the other 80 percent ($ 800). Plans with higher premiums generally have less coinsurance.: The annual out-of-pocket optimum is the most cost-sharing you will be accountable for in a year.
When you hit this limitation, the insurance provider will https://what-schedule-is-cocaine.drug-rehab-florida-guide.com/ pick up one hundred percent of your costs for the rest of the strategy year. Many enrollees never reach the out-of-pocket limitation but it can happen if a great deal of costly treatment for a serious accident or disease is required. Plans with greater premiums usually have lower out-of-pocket limitations.
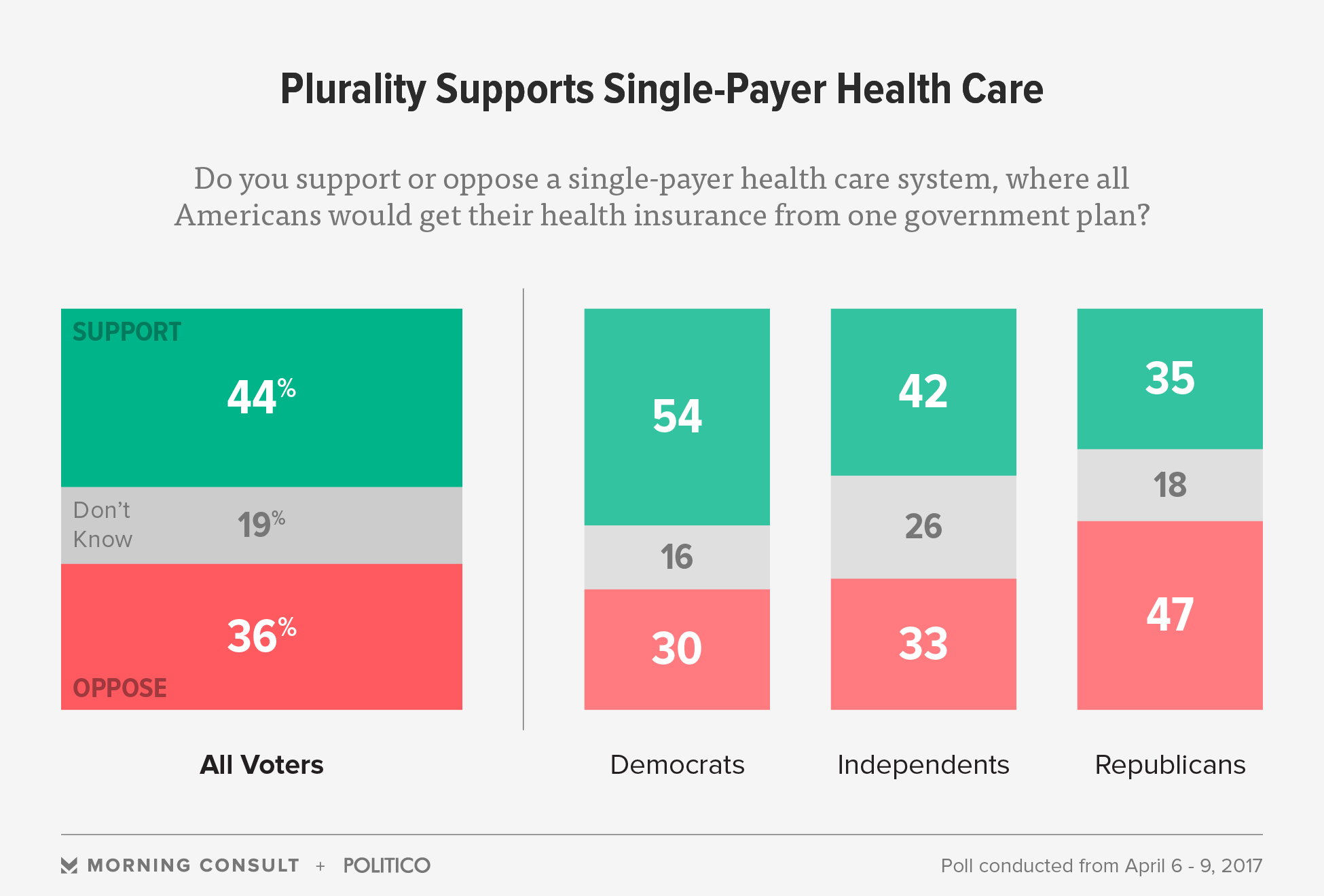
A 'covered advantage' usually describes a health service that is included (i.e., 'covered') under the premium for a provided medical insurance policy that is paid by, or on behalf of, the enrolled client. 'Covered' means that some part of the permitted expense of a health service will be considered for payment by the insurer.
For example, in a strategy under which 'immediate care' is 'covered', a copay may apply. The copay os an out-of-pocket expense for the patient (what is a deductible in health care). If the copay is $100, the client has to pay this quantity (usually at the time of service) and after that the insurance plan 'covers' the rest of the permitted expense for the urgent care service.

For instance, if a client has not yet satisfied a yearly deductible of $1,000, and the expense of the covered health service provided is $400, the patient will require to pay the $400 (often at the time of service). What makes this service 'covered' is that the cost counts towards the yearly deductible, so only $600 would remain to be paid by the client for future services before the insurer starts to pay its share.
Your premium, or just how much you spend for your medical insurance each month, covers some or all of the treatment you get everything from prescription drugs and medical professionals' sees to health improvement programs and customer care. A lot of people pick a medical insurance strategy based on monthly expense, as well as the advantages and medical services the plan covers.
The Basic Principles Of What Does A Health Care Administration Do
These out-of-pocket payments fall into different classifications and it is essential to know the distinctions in between them: Many medical insurance strategies consist of a deductible, which is the quantity you pay each year before your health insurance plan starts paying for covered services. For instance, if your plan has a $1,000 deductible, you will need to pay the first $1,000 of the expenses for the health care services you get.
A copay is a flat charge you pay to see a medical professional or get some other covered services, like a trip to the emergency clinic. For example, you may have a $20 copay to go see your physician, but a $200 copay if you visit the emergency situation space. Co-insurance is a portion you pay for some covered services, like a journey to a specialist or a particular medical test.
An out-of-pocket optimum is the most you will have to pay for your health care expenses throughout a strategy duration (normally a year) for covered services you receive from the doctors and health centers that participate in the strategy's network. No matter what, you will not pay more than this amount each strategy duration for covered services. how does universal health care work.
Payments by your health insurance company are generally based on discount rates the insurance company works out with physicians and medical facilities. Your insurer will pay your claim based upon the rate it has concurred on with the medical professionals, health centers, or healthcare center in your plan network.
Anyone interacting with the U.S. health care system is bound to encounter examples of unneeded administrative complexityfrom filling out duplicative intake types to transferring medical records in between providers to figuring out insurance expenses. This administrative intricacy, with its associated high expenses, is often mentioned as one reason the United States invests double the amount per capita on health care compared to other high-income countries despite the fact that usage rates are similar.
As healthcare costs continue to rise, a sensible starting point for potential savings is attending to waste. A 2010 report by the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) approximated that the United States invests about twice as much as required on BIR costs. That administrative excess presently totals up to $248 billion annually, according to CAP's estimations.
The 10-Second Trick For What Is Holistic Health Care
health care system. It first describes the elements of administrative costs and then presents quotes of the administrative costs borne by payers and providers. Finally, the problem brief describes how the United States can lower administrative costs through detailed reforms and incremental modifications to its health care system. A lot of the universal health care plans being talked about to broaden coverage and lower costs would decrease administrative costs through rate guideline, global budgeting, or simplifying the variety of payers.
The main components of administrative expenses in the U. what is universal health care.S. healthcare system consist of BIR expenses and health center or physician practice administration. The very first classification, BIR costs, belongs to the administrative overhead that is baked into customers' insurance coverage premiums and service providers' reimbursements. It includes the overhead expenses for the health insurance market and service providers' costs for claims submission, claims reconciliation, and payment processing.
To date, few studies have estimated the systemwide expense of healthcare administration extending beyond BIR activities. In a 2003 article in The New England Journal of Medicine, scientists Steffie Woolhandler, Terry Campbell, and David Himmelstein concluded that total administrative costs in 1999 amounted to 31 percent of overall healthcare expenditures or $294 billionroughly $569 billion today when adjusted for healthcare inflation.
Many studies of administrative costs limit their scope to BIR expenses. The BIR element of administration is most appropriate to systemwide reforms that seek to reduce the costs related to claims processing, billing rates, or health insurance coverage. The largest share of BIR expenses is attributable to insurer' revenues and overhead and to suppliers where BIR expenses include tasks such as record-keeping for claims submission and billing.
The procedure of claims denials has ended up being an industry unto itself, with private firms squeezing dollars out of Medicaid programs. One research study approximated that the aggregate value of challenged claims varies from $11 billion to $54 billion yearly. Claims can also be controlled to improve providers' or insurance providers' earnings by taping services rendered in optimum detail and overemphasizing the severity of patients' conditionsa practice referred to as upcoding.
The NAM released one of the most extensive reports on U.S. who led the reform efforts for mental health care in the united states?. administrative costs connected to billing and insurance coverage in 2010. In a synthesis of the literature on administrative costs, the NAM report concluded that BIR costs amounted to $361 billion in 2009about $466 billion in existing dollarsamong private insurers, public programs, and providers, totaling up to 14.4 percent of U.S.